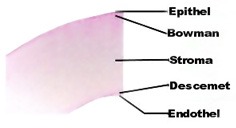
 Lasek (Laser Assisted Subepithelial Keratectomy)
Lasek (Laser Assisted Subepithelial Keratectomy)
Lasek operation method is usually performed in patients with a corneal layer that is too thin for Lasik operation, large pupils, very low or high diopters, abnormal corneal topography, retina problems or extremely dry eyes. Patients who play sports with close contact sometimes prefer the Lasek operation method, because no cutting is performed in this operation. In contrast to the Lasik method, the epithelial layer is removed in this method. A microkeratom is not used.
More corneal tissue is preserved with the Lasek operation method, yet the laser procedure and laser system is the same, and the outcome is equally well. The only disadvantage is the fact that the healing process lasts longer when compared with Lasik operation.
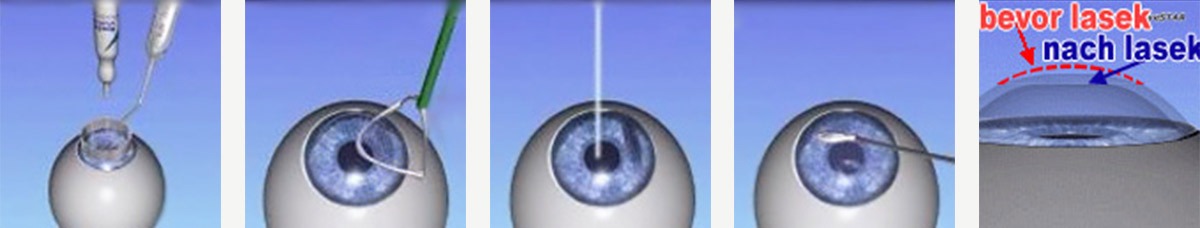
Lasek-operation is performed when the patient is lying down. After they are given a medical bonnet and overshoes, they are seated at the operation table, and their face is cleaned with a disinfectant substance. The eyes are anesthetized with eye drops so that the patient does not feel anything during the operation. The eyes are covered with a sterile foil to keep eyelashes away from the operation area. After a special device is placed on the eye to keep the eyelids open, the laser system and the data entered are rechecked by your operator. The eyes are then washed with water and dried. The patient is asked to look at the green light throughout the operation. A device in the form of a ring is placed on your cornea. A certain dose of alcohol is dropped into this ring, facilitating the removal of the epithelial layer from the stromal layer beneath. Subsequently, the epithelial layer is folded upwards and the laser beam is focused on the eye. The laser procedure is the same as the Lasik and only lasts for a few seconds. The type and time of the laser procedure depend on the degree of vision disorder and the diopter value. If the eye moves during the operation, the Eyetracker steps in. This system follows the eye movements sensitively. The laser stops automatically, when the patient is not looking at the green light. After the operator relocates the laser, the operation is continued. Afterwards, the epithelial layer that was folded upwards is brought back to its previous position.

Finally, a protective lens is placed in the eye. This lens should stay in the eye until the epithelial layer heals (approximately four days). These are soft lenses. They can be removed four days after the Lasek operation.
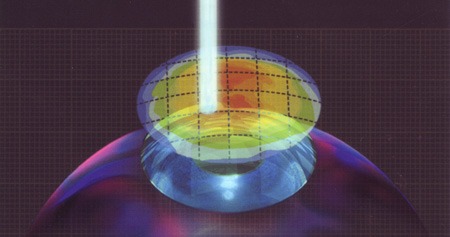
Lasek: the alternative to the Lasik method
According to our experience, patients usually think that the Laser operation will be difficult and painful, but this is not the case.
Lasik is an operation method which can be applied to most patients without any problems. However, there are also exceptions. If for example, the corneal layer too thin for a cut is or if the eyes are too dry, here Lasik cannot be carried out.
However, this is not a reason to renounce the patient a life without glasses. The alternative to the known operation method is called Lasek.
Lasek hardly differs from the sister method, merely the kind of the intervention in the cornea is different. With the Lasek method no so-called Flap is cut in the cornea, but merely the upper epithelium layer is removed. The microkeratome is not used with the Lasek.
Nevertheless, this is already nearly the only difference which an intervention with Lasek makes. All the other steps are the same with both Laser operation methods. The laser system, as well as the whole laser process, is equally applied with Lasek and Lasik. Only the healing process is a little more protracted with Lasek than with Lasik. Thus it can be that a Lasek patient disposes between one or two days of discomfort. However, also these fade away and the visual result to be expected is equally good with both eye Laser operation methods.
